
Snapshot Tomography: 3D Characterization of Powder at Unprecedented Speed
OTT1494
Applications
High-throughput 3D microscopic imaging of pharmaceutical powders, cosmetic powders, microplastics as well as biological cells, embryos, and organoids.
Target Problems
Optical tomography offers 3D structural and functional insights into complex specimens. Current techniques involve capturing numerous images during sample rotation, limiting imaging speed to approximately 10 tomograms/second.
Key Benefits
- Faster – Image 100x more samples per second in 3D.
- Multiple Contrasts – (Label-free) absorption, phase, and luminescence contrasts.
- Versatile – Detects 3D shapes, internal structures, impurities, contaminants, and foreign materials.
- Compact & Compatible – Compact module can be attached to an existing optical microscope.
Technology
This patented innovation – Snapshot Optical Tomography – performs 3D optical tomography in a single shot using various imaging contrasts. Image capture time is limited only by the camera frame rate (~several thousands of 3D tomograms/second).
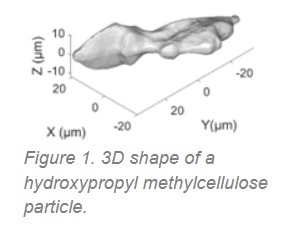
The system uses a micro-lens array combined with proprietary image reconstruction software to record 3D images at microscopic resolution at least up to 100 times faster than the current state of the art. It also can instantaneously capture 3D shape parameters of microscopic specimens such as sphericity, roundness, elongation ratio as well as volume, mass, density, composition, and heterogeneity.
Examples of applications include high-throughput 3D characterization of powders used in pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries as well as 3D printing. The technique is also being explored for label-free observation of single cell disease states, stem cell differentiation, embryo development.
Intellectual Property
Inventor
Yongjin Sung, Ph.D.Assoc., Professor in Biomedical Engineering and Mechanical Engineering, University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee
Sung Lab Website
